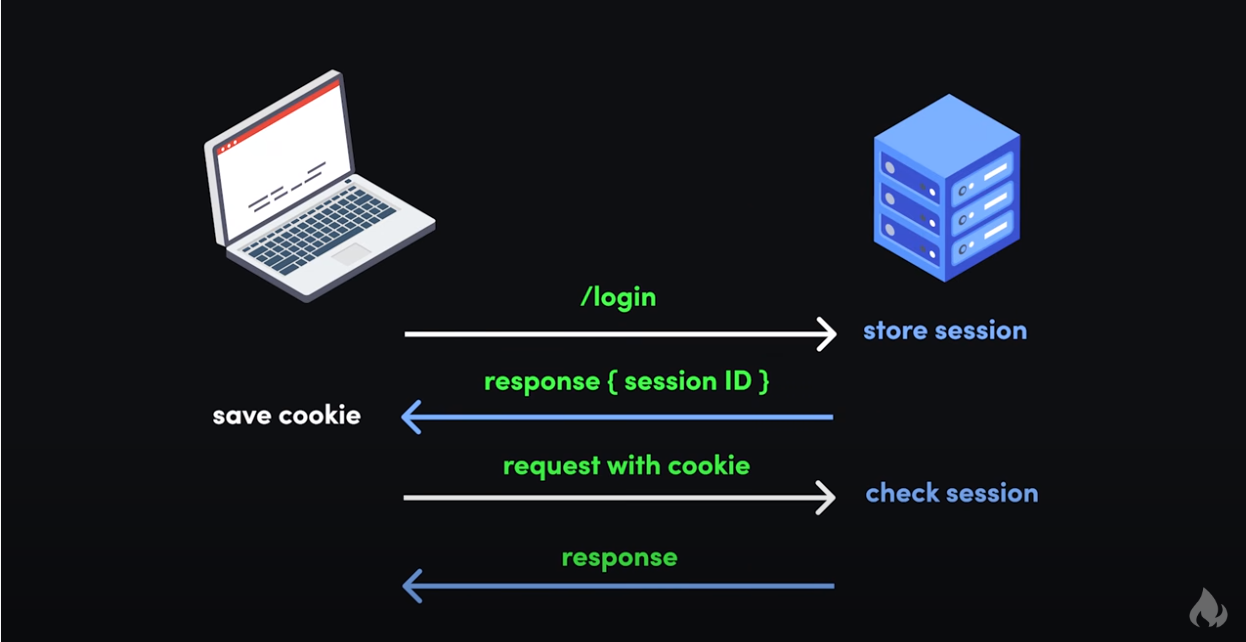
Client-Server Components
Client: A device or program that makes a request to a server to access resources or services.
Server: A system that provides resources or services to clients based on their requests.
This architecture is fundamental to web applications where the client is typically a web browser and the server is a web server hosting a website or web service.
HTTP Characteristics & Components

HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): The foundation of data communication on the Web.
- Stateless: Each request from a client to server is independent.
- Text-based protocol.
Components:
- Request: Made by the client to the server consisting of a request line, headers, and an optional body.
- Response: Sent by the server back to the client consisting of a status line, headers, and an optional body.
HTTP Request Format
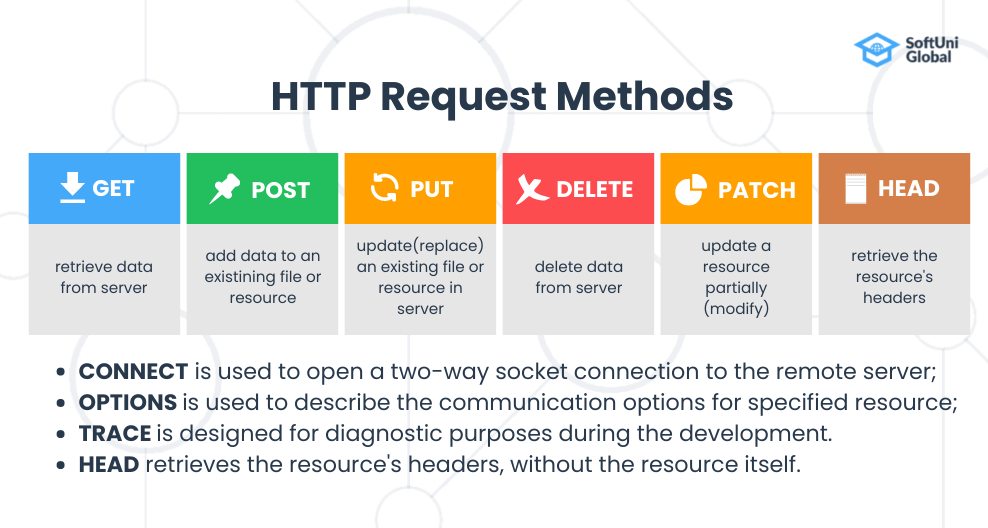
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) specifies a collection of request methods to specify what action is to be performed on a particular resource. The most commonly used HTTP request methods are GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE. These are equivalent to the CRUD operations (create, read, update, and delete).
- GET: GET request is used to read/retrieve data from a web server. GET returns an HTTP status code of 200 (OK) if the data is successfully retrieved from the server.
- POST: POST request is used to send data (file, form data, etc.) to the server. On successful creation, it returns an HTTP status code of 201.
- PUT: A PUT request is used to modify the data on the server. It replaces the entire content at a particular location with data that is passed in the body payload. If there are no resources that match the request, it will generate one.
- PATCH: PATCH is similar to PUT request but the only difference is it modifies a part of the data. It will only replace the content that you want to update.
- DELETE: A DELETE request is used to delete the data on the server at a specified location.
Request URL

Uniform Resource Identifier (URI): Identifies the resource on the server.
- Scheme: e.g., http or https.
- Host: Domain name or IP address.
- Path: Specific location/resource on the server.
- Query String: Additional data for the request.
JSON - Syntax, Arrays, Datatypes
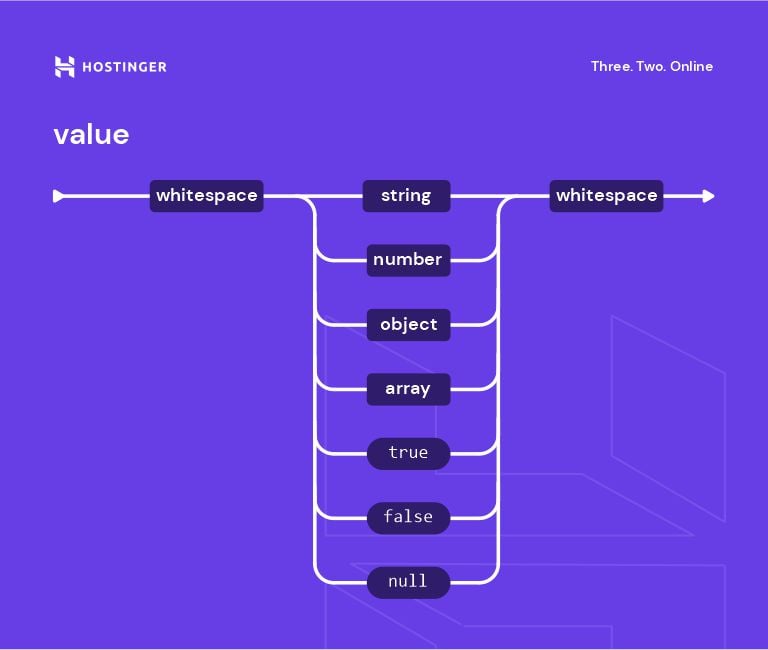
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): A lightweight format for data exchange.
Syntax:
- Objects are enclosed in {} with key-value pairs.
- Arrays are enclosed in [].
Data Types:
- Strings
- Numbers
- Booleans
- Null
- Objects
- Arrays
REST (Representational State Transfer)

REST: An architectural style that can be applied to web services to create and enhance properties like performance, scalability, and modifiability.
RESTful web services are generally highly scalable, light, and maintainable, and are used to create APIs for web-based applications. It exposes API from an application in a secure and stateless manner to the client. The protocol for REST is HTTP.
REST emerged as the predominant Web service design model just a couple of years after its launch, measured by the number of Web services that use it.
Advantages of REST:
- Simplicity: RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), which are easy to understand and use.
- Statelessness: Each request from a client to the server must contain all the information needed to understand and complete the request.
- Scalability: Due to its stateless nature, REST can scale more efficiently by using multiple servers.
- Flexibility: REST APIs can handle multiple types of calls, return different data formats, and change structurally with the correct use of hypermedia.
Search Engine, Web Crawling, SEO

Search Engine: A software system designed to search for information on the World Wide Web. Examples include Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
Web Crawling:
Web crawlers or spiders are automated scripts that browse the web and index web pages. The crawlers work by visiting a website, downloading its content, and following all the links on the page to find other pages.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization):
SEO involves optimizing web pages to rank higher in search engine results, thus increasing the amount of organic (non-paid) traffic the website receives.
- On-page SEO: Refers to the content and HTML source code of a page that can be optimized.
- Off-page SEO: Involves promotion methods beyond website design to improve search rankings, like backlinking.
SSL and How it Works

SSL (Secure Sockets Layer): A standard security protocol for establishing encrypted links between a web server and a browser in an online communication.
How SSL Works:
- The client sends a request to the server for a secure session.
- The server sends its SSL certificate to the client, which contains the server's public key.
- The client validates the SSL certificate against trusted authorities.
- If the certificate is valid, the client generates a session key, encrypts it with the server's public key, and sends it to the server.
- The server decrypts the session key using its private key, establishing a secure session.
- All subsequent communication is encrypted with the session key.
SSL is essential for protecting sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, as it is transmitted over the Internet.